Stud Roll Forming Machine: Precision Engine for Construction Framing
Stud roll forming machines represent specialized equipment designed to manufacture the fundamental vertical framing components – studs – used in modern light-gauge steel (LGS) construction. These machines transform galvanized steel coils into standardized C-shaped or U-shaped profiles that form the skeletal framework of walls, partitions, and structural elements in commercial, residential, and industrial buildings. As modular and prefabricated construction gains momentum globally, stud roll forming technology has become increasingly vital for efficient, precise, and cost-effective building systems.
Technical Process and Machine Configuration
The stud roll forming process follows a continuous, automated sequence that ensures consistent dimensional accuracy and material properties:
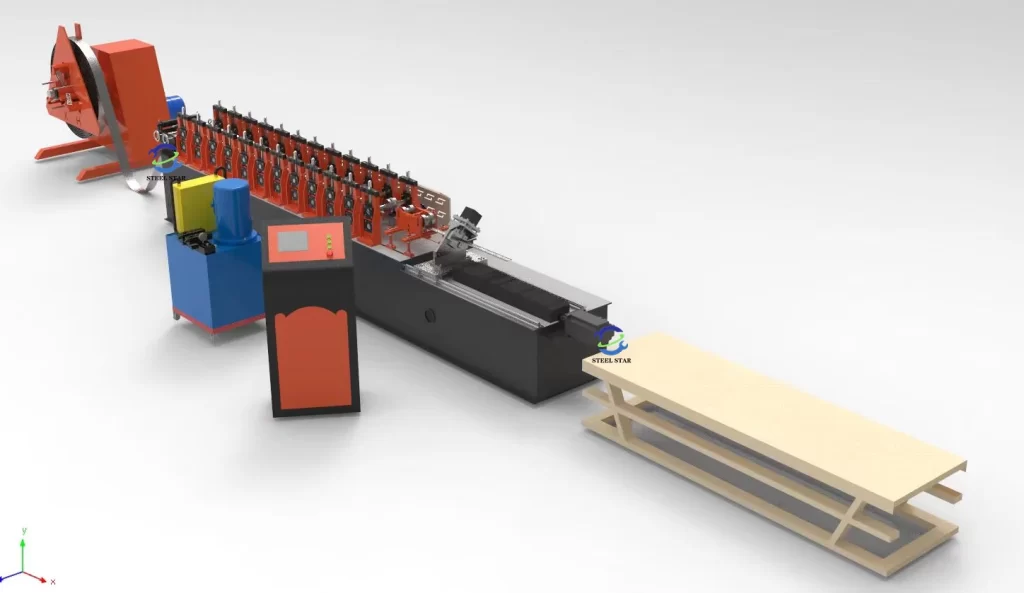
Primary Machine Components:
- Coil Loading System – Hydraulic or motorized decoiler handling coils up to 5 tons
- Pre-punching Station – Servo-controlled punching units creating service holes, screw slots, and alignment notches
- Roll Forming Section – 12-20 forming stations gradually shaping the profile
- Cut-off Mechanism – Hydraulic flying cut system for precise length control (±0.5mm)
- Output Handling – Automatic stacking, counting, and bundling systems
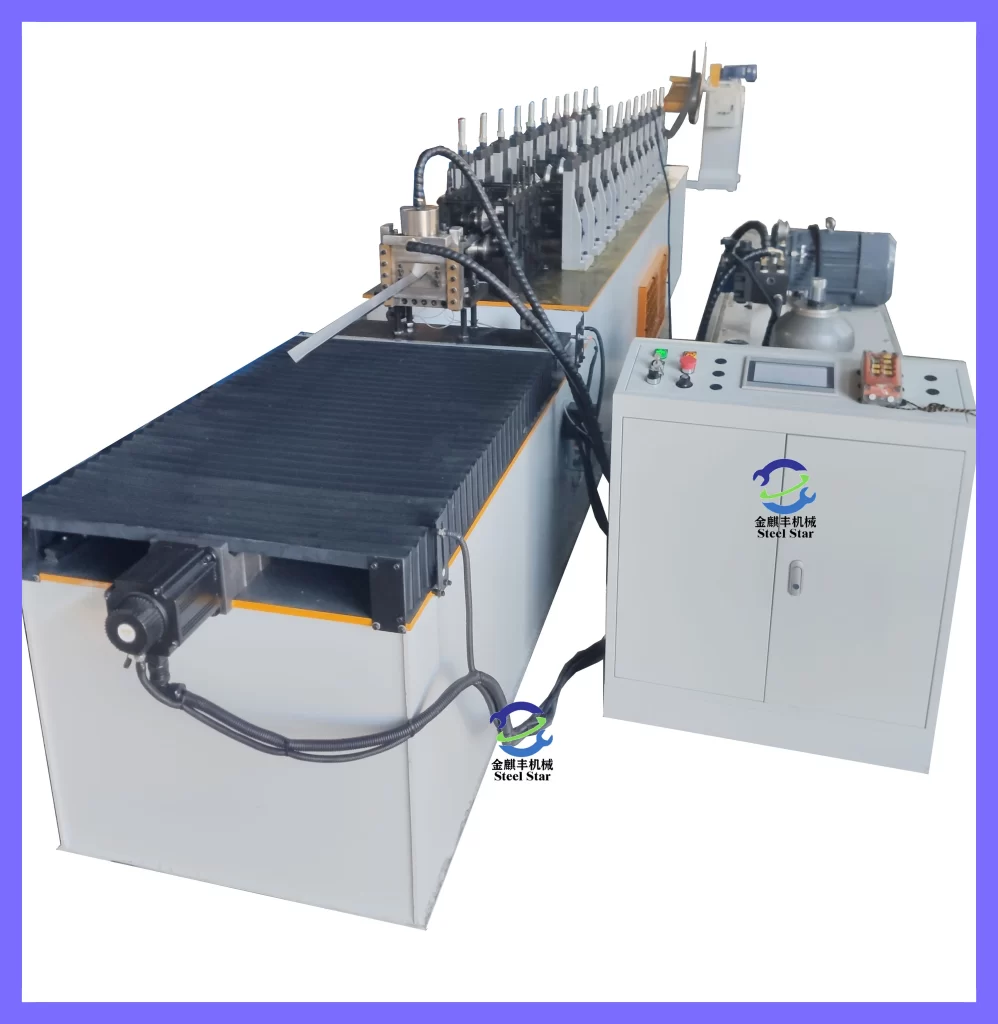

Standard Production Specifications:
- Material thickness: 0.8mm to 2.5mm
- Web heights: 70mm to 250mm
- Flange widths: 40mm to 75mm
- Production speed: 30-100 meters per minute
- Standard lengths: 2.4m to 12m
Types and Applications
Stud roll forming machines are categorized by their specific applications:
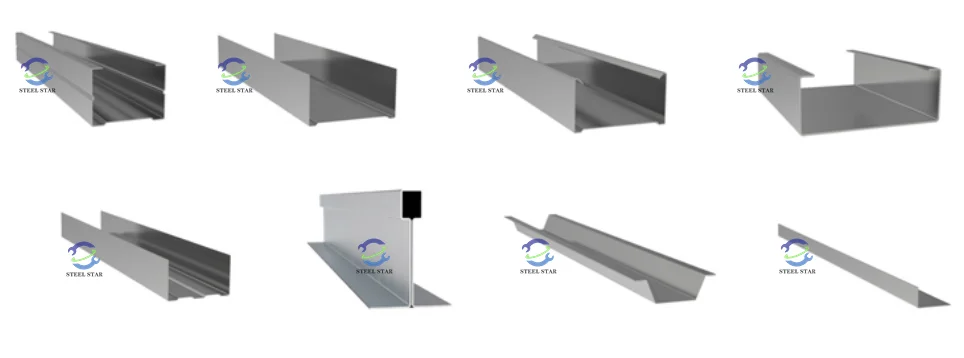
Wall Stud Machines
- C-section producers for vertical load-bearing members
- Track/runner formers for top and bottom plates
- Jamb stud formers for door and window openings
Specialized Profile Machines
- U-channel formers for bridging and blocking
- Furring channel machines for ceiling systems
- Header/trimmer machines for openings
Advanced Configuration Machines
- Multi-profile lines with quick-change capabilities
- Integrated systems combining stud forming with cutting, notching, and welding
- Custom-profile machines for proprietary building systems
Technical Advantages and Industry Impact
Construction Efficiency Benefits
- Dimensional Precision – Consistent profiles ensuring perfect fit-up during assembly
- Material Optimization – Reduced waste through precise cutting and nesting capabilities
- Production Speed – High-volume output meeting large project demands
- Quality Consistency – Uniform mechanical properties throughout production runs
Economic Advantages
- 40-60% faster framing installation versus traditional methods
- Reduced labor requirements on construction sites
- Lower transportation costs through efficient bundling
- Minimized material waste (typically <3%)
Sustainability Contributions
- High recycled content in galvanized steel
- Complete recyclability at end of life
- Reduced construction waste generation
- Energy-efficient manufacturing process
Key Selection Criteria
Technical Considerations
- Profile range and changeover flexibility
- Material grade capabilities (G550, G500, G300)
- Tooling quality and maintenance requirements
- Automation level and control sophistication
Operational Factors
- Production capacity matching business volume
- Floor space and utility requirements
- Operator skill requirements and training needs
- Maintenance accessibility and service support
Economic Evaluation
- Capital investment versus production ROI
- Operating costs including tooling maintenance
- Energy consumption and efficiency metrics
- Expected service life and depreciation schedule
Modern Technological Features
Advanced Control Systems
- PLC with touch-screen HMI interfaces
- Servo-driven precision positioning
- Automatic fault detection and diagnosis
- Production data logging and reporting
Quality Assurance Integration
- Laser measurement for dimensional verification
- Vision systems for defect detection
- Real-time thickness monitoring
- Statistical process control capabilities
Automation Enhancements
- Robotic stacking and packaging
- Automated coil loading and splicing
- Tool-less changeover systems
- RFID-tagged bundle identification
Industry Applications and Market Trends
Construction Sector Applications
- Commercial office buildings and retail spaces
- Multi-story residential construction
- Healthcare and educational facilities
- Industrial warehouses and manufacturing plants
- Modular and prefabricated building systems
Emerging Market Trends
- Green Building Integration – Alignment with LEED and BREEAM certifications
- Digital Workflow Connectivity – BIM integration and digital fabrication
- Customization Demand – Architecturally specific profile requirements
- Seismic and Wind Resistance – Enhanced engineering for extreme conditions
- Fire-Rated Systems – Integration with fire protection requirements
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Routine Maintenance Protocol
- Daily cleaning and lubrication procedures
- Weekly alignment and calibration checks
- Monthly wear inspection and adjustment
- Quarterly comprehensive maintenance
Tooling Management
- Proper storage and handling procedures
- Regular sharpening and refurbishment
- Inventory management for critical spares
- Lifecycle tracking and replacement planning
Operator Training Requirements
- Machine operation and safety procedures
- Basic troubleshooting skills
- Quality inspection techniques
- Preventive maintenance competencies
Future Developments and Innovations
Technological Advancements
- AI-powered predictive maintenance systems
- Augmented reality for operator assistance
- Advanced servo technology for higher precision
- Energy recovery and sustainable operation features
Market Evolution
- Growing adoption in emerging economies
- Increased customization capabilities
- Integration with robotic assembly systems
- Development of hybrid material capabilities
Industry Standards Development
- Enhanced international quality standards
- Improved safety and ergonomic features
- Environmental compliance advancements
- Digital certification and traceability systems
Stud roll forming machines have revolutionized modern construction methodologies by providing a reliable, efficient, and precise method for producing essential building components. As the construction industry continues to embrace steel framing for its durability, sustainability, and economic advantages, these machines will play an increasingly crucial role in global building infrastructure development.
The successful implementation of stud roll forming technology requires careful consideration of technical specifications, operational requirements, and economic factors. With proper selection, maintenance, and operation, these machines can deliver decades of reliable service while providing the construction industry with the high-quality, consistent components needed for modern building projects.
As technology advances, we can expect continued innovation in automation, precision, and flexibility, further solidifying the position of stud roll forming machines as indispensable tools in the construction industry’s ongoing evolution toward more efficient, sustainable, and resilient building practices.
Website:
www.greatforming.com (English)
www.arabicgreatforming.com (عربي)
www.russiangreatforming.com(Русский)
www.spanishgreatforming.com(Español)
www.frenchgreatforming.com(Français)
www.portuguesegreatforming.com(Portuguese)

