Wall Sheet Roll Forming Machine: Precision Engineering for Modern Building Envelopes
A wall sheet roll forming machine is a highly specialized industrial system designed to continuously transform flat metal coils into profiled wall cladding and sandwich panels. As a critical component in modern construction and prefabricated building technologies, these machines produce the architectural panels that define contemporary building exteriors while providing essential structural integrity, thermal insulation, and weather protection. The technology represents the intersection of precision engineering, material science, and architectural design.
Technical Process and Machine Configuration
The manufacturing process employs continuous cold roll forming technology where metal coils—typically pre-painted galvanized steel, aluminum, or stainless steel—are progressively shaped through multiple forming stations.
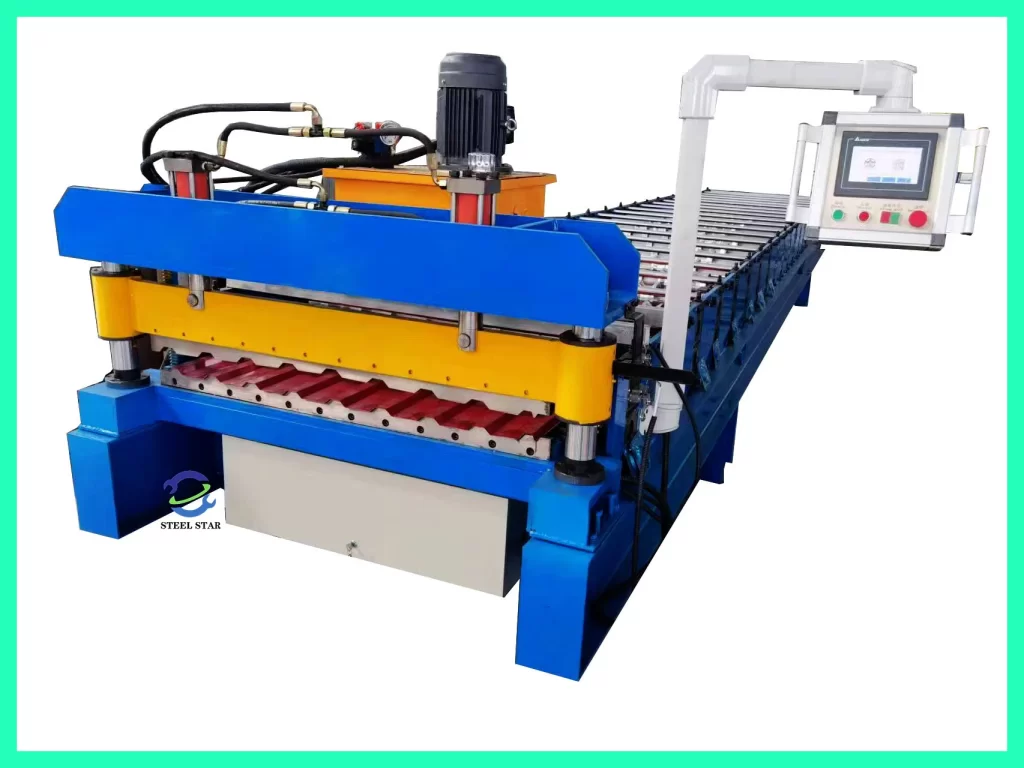
Core System Components:
- Uncoiling System: Heavy-duty decoiler with automatic coil loading and edge alignment
- Pre-punching Station: CNC-controlled punching units for creating service openings and fastener holes
- Roll Forming Section: 12-25 forming stations with precision-ground hardened steel rolls
- Insulation Integration: Optional polyurethane/PIR foam injection systems for sandwich panels
- Cut-off Mechanism: Hydraulic flying cut with ±0.5mm length accuracy
- Output Handling: Automated stacking with interleaf paper or protective film application
Production Specifications:
- Material thickness: 0.4mm to 1.2mm
- Panel width: 600mm to 1200mm
- Profile depth: 15mm to 100mm
- Production speed: 15-40 meters per minute
- Standard lengths: Up to 16 meters (customizable)
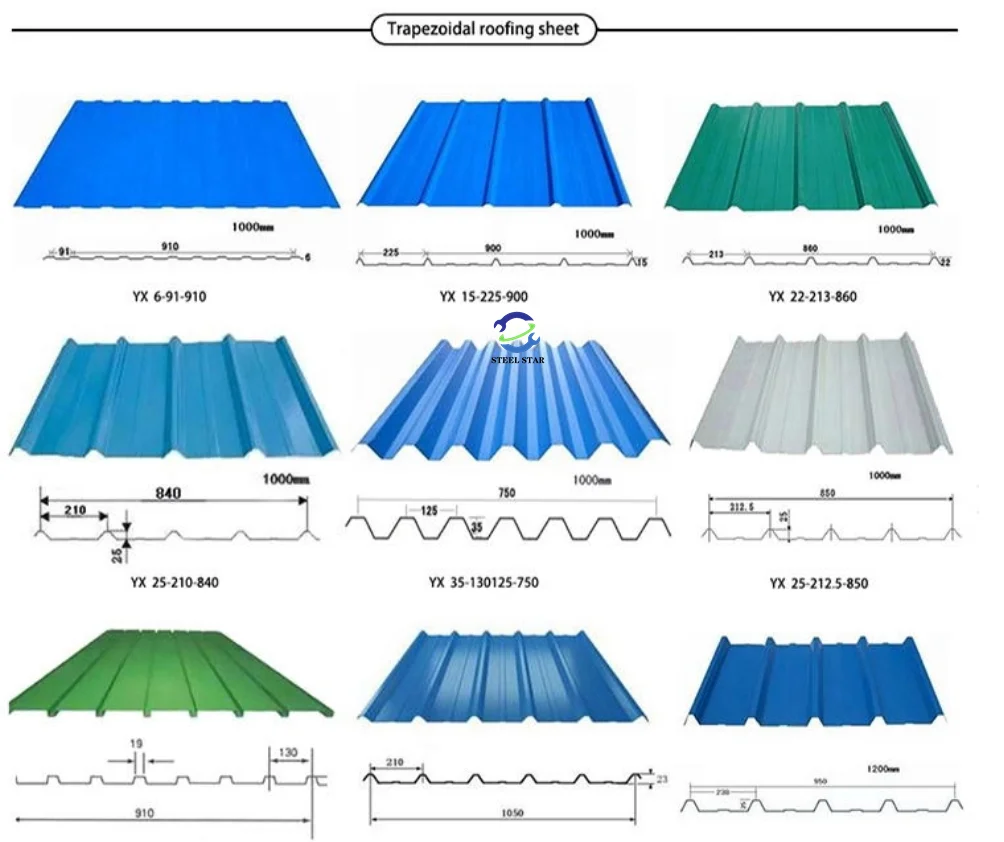
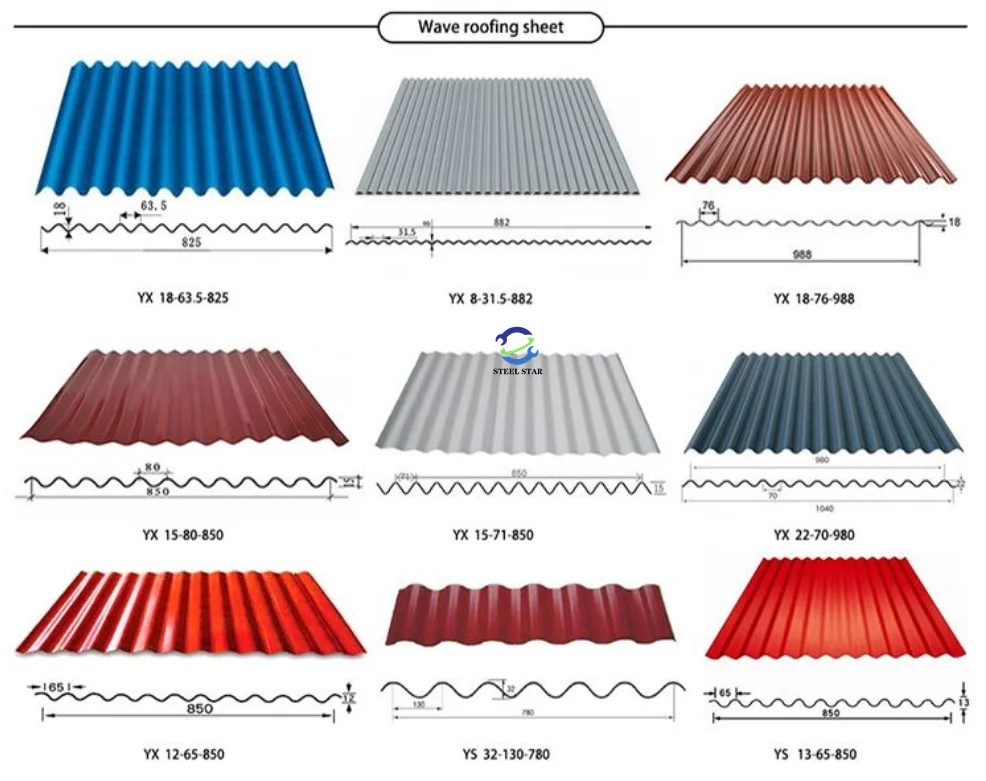
Machine Types and Panel Varieties
Single-Skin Panel Machines
- Produce corrugated, trapezoidal, or custom architectural profiles
- Applications: Industrial buildings, warehouses, secondary cladding
Sandwich Panel Production Lines
- Integrated systems applying PUR/PIR/rock wool insulation between metal skins
- Applications: Cold storage, clean rooms, energy-efficient buildings
Composite Panel Systems
- Combine different metals or integrate functional layers
- Applications: Specialized industrial facilities, high-performance buildings
Advanced Configuration Machines
- Quick-change profile systems for flexible production
- Integrated embossing and printing capabilities
- Multi-width adjustable forming technology
Technical Advantages and Construction Benefits
Structural and Performance Benefits:
- Weather Integrity: Interlocking panel designs ensure water-shedding capabilities
- Thermal Efficiency: Continuous insulation layers eliminate thermal bridging
- Structural Performance: High strength-to-weight ratios for spanning capabilities
- Fire Resistance: Incorporation of non-combustible insulation materials
Economic and Operational Advantages:
- Reduced on-site labor through prefabrication
- Faster enclosure of building structures
- Minimal material waste (typically <3%)
- Consistent quality control in factory conditions
Sustainability Features:
- High recycled metal content utilization
- Integration of sustainable insulation materials
- Energy-efficient production processes
- Complete recyclability at end of service life
Industry Applications and Architectural Integration
Commercial Construction:
- Office buildings and retail centers
- Healthcare and educational facilities
- Airport terminals and transportation hubs
Industrial Applications:
- Manufacturing plants and logistics centers
- Food processing facilities
- Pharmaceutical production environments
Specialized Uses:
- Clean rooms and laboratory facilities
- Sports complexes and entertainment venues
- Modular and temporary structures
Key Selection Criteria for Investment
Technical Considerations:
- Profile design flexibility and changeover time
- Material grade capabilities (AZ150, G550, etc.)
- Insulation integration options and thickness range
- Surface protection requirements (PVDF, HDPE, etc.)
Operational Requirements:
- Production capacity alignment with market demand
- Factory space and utility infrastructure needs
- Operator skill requirements and training systems
- Maintenance protocols and technical support availability
Economic Evaluation Factors:
- Capital investment versus production ROI
- Tooling costs and maintenance expenses
- Energy consumption and operational efficiency
- Expected service life and upgrade pathways
Modern Technological Features
Advanced Control Systems:
- Multi-axis servo control for synchronized operations
- Vision systems for surface defect detection
- Real-time thickness and profile monitoring
- Cloud-based production data management
Quality Assurance Technologies:
- Laser measurement for dimensional verification
- Adhesive application monitoring systems
- Insulation density and distribution control
- Automated sample testing and certification
Production Integration:
- Robotic material handling and packaging
- Automated color change and surface treatment
- RFID tracking for customized production batches
- MES (Manufacturing Execution System) integration
Market Trends and Industry Evolution
Digital Transformation:
- BIM-compatible panel design and fabrication
- Automated order-to-production workflow systems
- Augmented reality for installation guidance
Performance Enhancement:
- Enhanced fire-rated panel systems
- Improved acoustic performance profiles
- Hurricane and seismic-resistant designs
- Hygienic surface technology for specialized environments
Maintenance and Operational Excellence
Preventive Maintenance Protocol:
- Daily cleaning and lubrication schedules
- Weekly roll alignment and pressure verification
- Monthly wear assessment and adjustment
- Annual comprehensive overhaul and recalibration
Tooling Management:
- Precision grinding and refurbishment cycles
- Inventory management for critical components
- Lifecycle tracking and replacement planning
- Storage and handling best practices
Operator Competency Development:
- Machine operation and safety certification
- Quality inspection and process control training
- Basic troubleshooting and maintenance skills
- Continuous improvement methodology training

Future Developments and Innovation Pathways
Technological Advancements:
- AI-driven predictive maintenance and quality control
- 3D laser profiling for complex architectural forms
- Nanotechnology coatings integration during forming
- Energy-harvesting panel system production
Sustainable Manufacturing:
- Zero-waste production system development
- Low-energy curing and forming technologies
- Bio-based insulation material integration
- Closed-loop water and energy systems
Industry 4.0 Integration:
- Digital twin technology for virtual commissioning
- Blockchain-enabled supply chain traceability
- IoT-enabled smart panel production
- Automated adaptive manufacturing systems
Wall sheet roll forming machines represent the pinnacle of construction manufacturing technology, enabling the production of high-performance building envelopes that define modern architecture. These sophisticated systems combine precision engineering with material innovation to create products that address the critical challenges of energy efficiency, durability, and architectural expression in contemporary construction.
The selection and operation of these machines require careful consideration of technical capabilities, market requirements, and long-term business strategy. As the construction industry continues to evolve toward greater prefabrication, sustainability, and performance-based design, wall sheet roll forming technology will remain at the forefront of building envelope solutions.
Future advancements will likely focus on greater customization capabilities, enhanced sustainability features, and deeper digital integration throughout the design, manufacturing, and installation processes. For manufacturers and contractors committed to excellence in building envelope solutions, investment in advanced wall sheet roll forming technology represents both a competitive necessity and a strategic opportunity to lead in the evolving construction landscape.
The continued development of these machines will play a crucial role in addressing global challenges of urbanization, climate resilience, and resource efficiency, making them not just industrial equipment, but essential tools for building a sustainable future.
Website:
www.greatforming.com (English)
www.arabicgreatforming.com (عربي)
www.russiangreatforming.com(Русский)
www.spanishgreatforming.com(Español)
www.frenchgreatforming.com(Français)
www.portuguesegreatforming.com(Portuguese)

