What is a Roof Sheet Bending Machine?
A Roof Sheet Bending Machine, commonly known as a roll forming machine for roofing profiles, is a continuous, automated production line. It progressively shapes a flat strip of metal (typically steel, aluminum, or stainless steel) through a series of roller dies to create long, consistent panels with specific cross-sectional profiles. Unlike press braking, which bends discrete sections, roll forming produces a seamless, uninterrupted length of profiled sheet, making it ideal for long roofing spans.
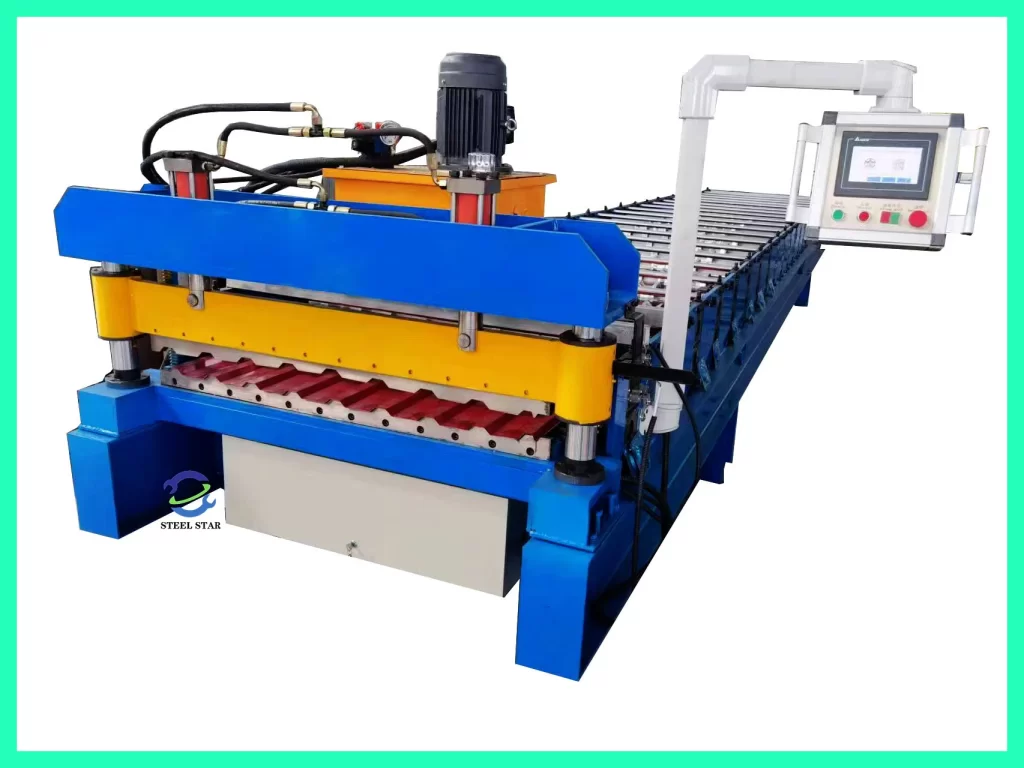
Core Components and Their Functions
A typical roof sheet roll forming line is an integrated system comprising several key stations:
Decoiler/Uncoiler: The starting point, holding the master coil of pre-painted (e.g., PPGI, PPGL) or galvanized steel. It feeds the metal strip into the line under controlled tension.
Entry Guide & Flattener/Leveler: This section aligns the strip and removes any coil curvature or minor imperfections, ensuring perfectly flat material enters the forming process—a critical step for profile accuracy.
Pre-Punching/Notching Unit (Optional but Common): For panels requiring screw ports, drainage holes, or interlocking features, a synchronized punching station perforates the flat strip before it is formed.
The Roll Forming Mill (The Heart): This is a sequential set of stands, each containing a pair or cluster of meticulously engineered roller dies. Each stand incrementally bends the metal strip by a few degrees, gradually forming the final profile—from simple corrugations to complex trapezoidal or standing seam designs. The number of stands varies with profile complexity.
Cutting System: Once the profile is fully formed, a precision cutting mechanism—usually a flying cut-off saw or hydraulic shear—cuts the continuous panel to the pre-set length without stopping the line. The cutter synchronizes its speed with the moving sheet.
Run-Out Table & Stacker/Automatic Unloader: The finished, cut-to-length panels are conveyed to the end of the line, where they are automatically stacked, counted, and bundled for packaging and shipment.
PLC Control System: The brain of the machine. A Programmable Logic Controller governs the entire line—speed, feed length, cutting sequence, and synchronization of all components. Modern interfaces allow for easy profile selection and parameter adjustment.
The Roll Forming Process: A Step-by-Step Flow
Material Loading: A master coil is mounted onto the decoiler. The leading edge of the strip is fed through the entry guides.
Pre-Processing: The strip passes through the leveling rolls and, if equipped, the punching station, where features are added in the flat state.
Progressive Forming: The metal enters the roll forming mill. As it progresses through each successive stand of roller dies, it is bent incrementally. For example, the edges begin to curl upwards to form ribs or interlocks, and the central section may form a trapezoidal crest.
Final Profile & Cutting: Upon exiting the final forming stand, the panel has achieved its complete cross-section. The flying cut-off system cleanly shears it to the exact required length (e.g., 2 meters, 8 meters) while the line runs continuously.
Output Handling: The finished panels glide onto the run-out table and are automatically stacked in a neat pile, ready for manual or robotic handling.
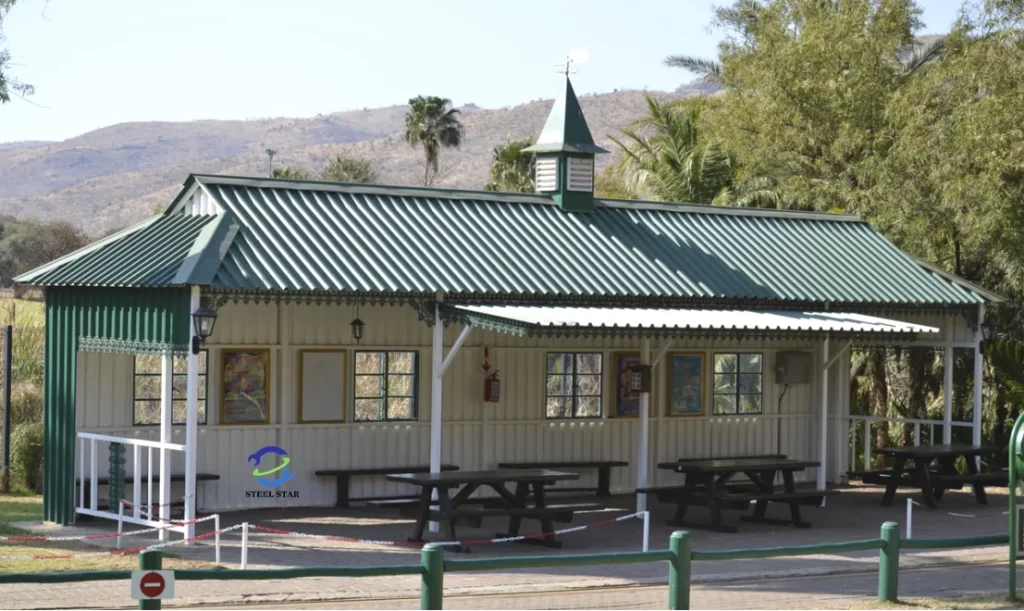

Common Roofing Profiles Produced
These machines are versatile and can be tooled to produce a vast array of profiles, including:
Corrugated Sheets: The classic wavy profile, offering simple strength and drainage.
Trapezoidal/Box Profile Panels: Characterized by broad, flat pans and steep sides, providing high load-bearing capacity, commonly used for industrial roofs and walls.
Standing Seam Roof (SSR) Panels: The premium choice for commercial and architectural roofing. The machine forms high vertical seams that interlock mechanically or via seaming tools on-site, creating a weather-tight, fastener-free roof surface that allows for thermal expansion.
Tile Effect Profiles: Formed to mimic the appearance of traditional clay or concrete tiles, offering a modern alternative with metal’s benefits.
Key Advantages of Roll Forming for Roof Sheets
High-Speed, Continuous Production: Capable of producing tens of meters of finished panel per minute, making it highly efficient for large-scale projects.
Exceptional Consistency & Quality: Every panel in a production run is identical, with precise tolerances on dimensions and profile shape, ensuring perfect fit during installation.
Material Efficiency: Minimal waste is generated, as cutting is precise and the process uses the entire strip. Scrap from the sides (edge trim) is minimal and recyclable.
Strength Enhancement: The cold-forming process work-hardens the metal at the bends, increasing the panel’s stiffness and load-bearing capability compared to the flat sheet.
Website:
www.greatforming.com (English)
www.arabicgreatforming.com (عربي)
www.russiangreatforming.com(Русский)
www.spanishgreatforming.com(Español)
www.frenchgreatforming.com(Français)
www.portuguesegreatforming.com(Portuguese)

