Shutter Door Roll Forming Machine: Engineering Efficiency in Modern Closures
Shutter door roll forming machines represent a sophisticated class of industrial manufacturing equipment designed to transform metal coils into precise, interlocking shutter door profiles through continuous cold-forming processes. This article examines the operational principles, technical configurations, production capabilities, and industrial significance of these specialized machines, which have revolutionized the architectural closure industry through automated, high-volume production of consistent shutter door components.
1. Introduction to Roll Forming Technology
Roll forming is a continuous bending operation where a long strip of metal (typically coiled steel, aluminum, or PVC-coated materials) passes through successive sets of rolls, each performing an incremental part of the bend until the desired cross-sectional profile is achieved. When applied to shutter door production, this technology enables the creation of precisely engineered slats or louvers with interlocking mechanisms, consistent dimensions, and structural integrity essential for security, insulation, and durability in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
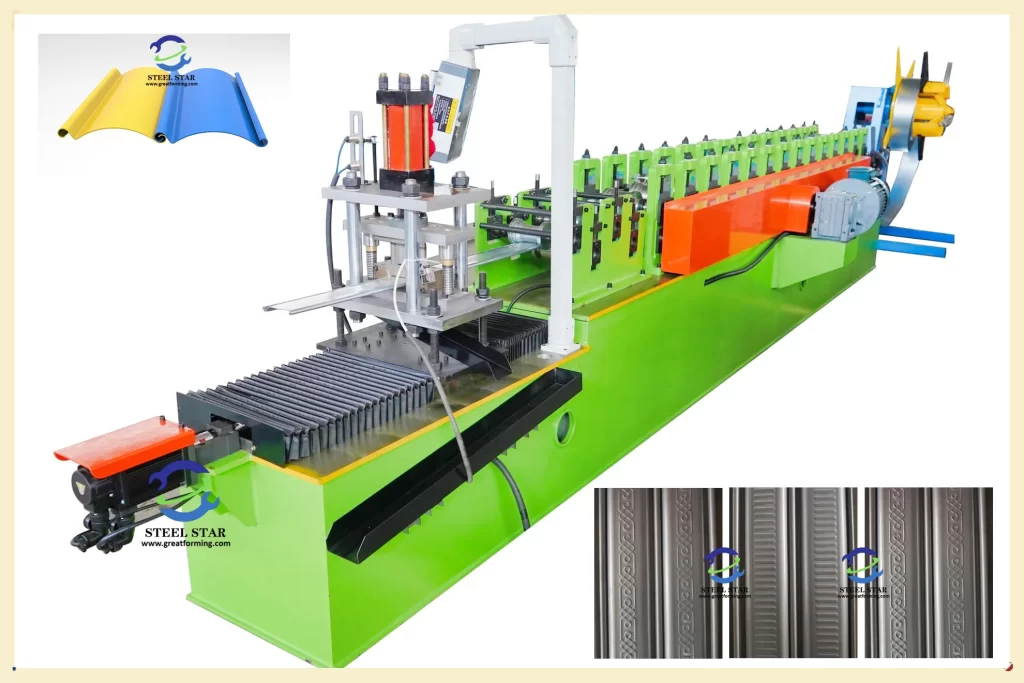

2. Working Principle and Machine Architecture
2.1 Core Operational Sequence
A shutter door roll forming machine follows a systematic production sequence:
- Decoiling & Straightening: The metal coil (typically 0.3-1.2mm thickness) is mounted on an uncoiler, straightened through leveling rollers, and fed into the system at controlled tension.
- Pre-Punching/Notching Station (Optional): Some designs incorporate punching units to create cutouts, hinge holes, or decorative patterns before forming.
- Roll Forming Section: The heart of the machine where 10-30 pairs of precisely engineered roll stands progressively shape the flat strip into the final shutter profile. Each stand contributes incremental bends, with the number of stands determined by profile complexity.
- Cutting System: A flying cut-off mechanism (hydraulic or servo-driven) accurately cuts the continuously formed profile to predetermined lengths without stopping the production line.
- Output & Stacking: Finished shutter slats are conveyed to stacking systems or transfer mechanisms for packaging or direct assembly.
2.2 Key Machine Components
- Heavy-duty frame: Rigid construction to maintain alignment under operational stresses
- Tooling stations: Interchangeable precision rollers made from hardened tool steel or carbide
- Drive system: Typically AC vector drives with reduction gearboxes for synchronized operation
- Control system: PLC-based with HMI interface for parameter setting and monitoring
- Hydraulic/pneumatic systems: For cutting operations and clamping functions
- Guiding systems: Edge guides and entry tables ensuring proper material alignment
3. Technical Specifications and Capabilities
3.1 Production Parameters
- Material compatibility: Galvanized steel, aluminum alloys, pre-painted coils, PVC-coated metals
- Standard thickness range: 0.3mm to 1.5mm
- Production speed: 15-45 meters per minute (depending on profile complexity)
- Cutting length accuracy: ±0.5mm to ±1.0mm
- Profile width: Typically 50-150mm for individual shutter slats
- Length customization: Variable from 500mm to 3000mm+ per slat
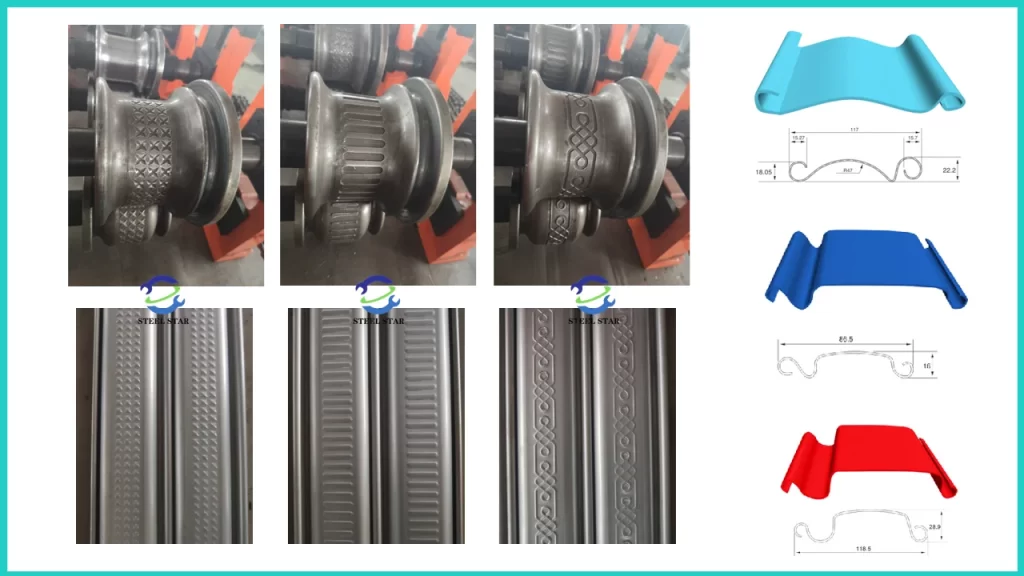
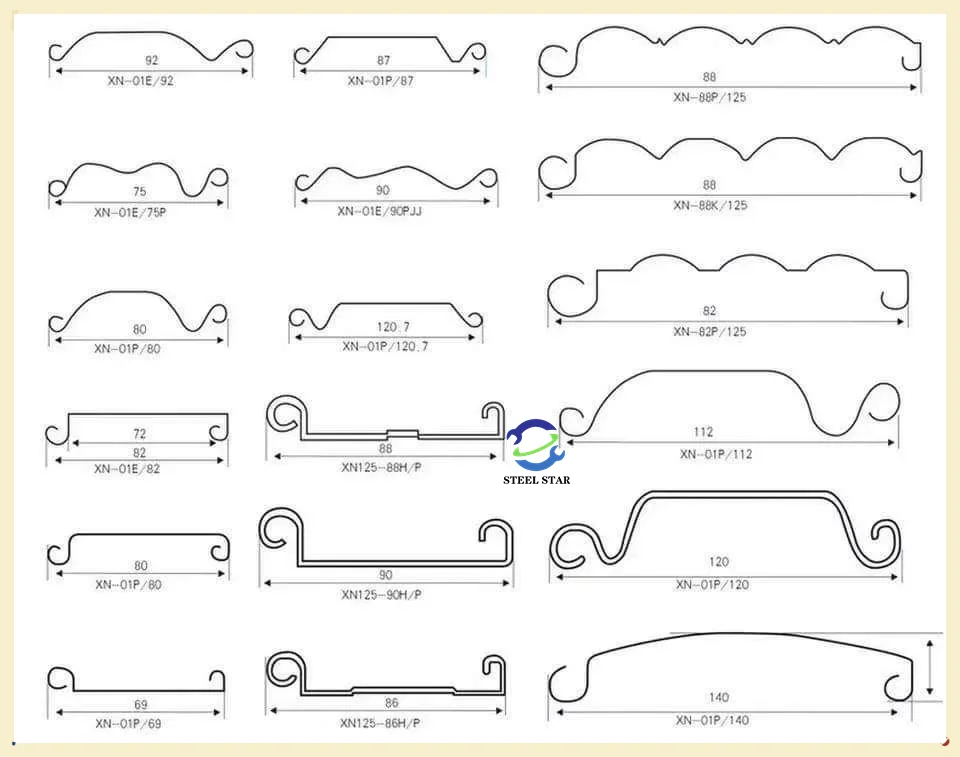
3.2 Profile Design Variants
Modern machines can produce multiple shutter door profiles:
- Traditional interlocking designs: With S-shaped or C-shaped joining edges
- Thermal break profiles: Incorporating insulation channels for energy efficiency
- Decorative patterns: Embossed or curved louvers for aesthetic applications
- Security-enhanced designs: Reinforced profiles with anti-lift features
- Commercial/industrial variants: Heavier gauges with structural reinforcements
4. Advantages Over Alternative Manufacturing Methods
The adoption of roll forming technology for shutter door production offers significant benefits:
4.1 Production Efficiency
- Continuous operation enables high-volume output (typically 500-2000 slats per 8-hour shift)
- Minimal material waste compared to stamping or individual pressing methods
- Reduced labor requirements through automation
4.2 Quality Consistency
- Exceptional dimensional accuracy across entire production runs
- Uniform mechanical properties with minimal residual stresses
- Consistent surface finish without the handling marks common in manual methods
4.3 Economic Benefits
- Lower per-unit production costs at medium to high volumes
- Reduced tooling costs compared to dedicated stamping dies
- Quick changeover between profiles (typically 1-2 hours)
- Energy efficiency through cold-working process

5. Integration with Complete Production Lines
Advanced shutter door manufacturing systems integrate roll forming machines with auxiliary equipment:
- Automated coil handling: Cranes and loading systems for efficient material supply
- Pre-treatment systems: Cleaning or chemical treatment stations
- In-line punching/embossing: For hinge holes, reinforcement, or decoration
- Powder coating lines: For finishing after forming
- Assembly stations: Automated sorting and assembly of complete shutter doors
- Packaging systems: Automated bundling and wrapping for shipment
6. Technological Advancements and Industry 4.0 Integration
Modern shutter door roll forming machines incorporate cutting-edge technologies:
- Servo-electric cut-off systems: Providing enhanced precision and flexibility
- Laser measurement systems: For real-time profile verification and quality control
- Predictive maintenance: IoT sensors monitoring vibration, temperature, and wear
- Digital twin technology: Simulating production runs before physical setup
- Automated tool change systems: Reducing changeover time between profiles
- Energy recovery systems: Capturing and reusing braking energy
7. Market Applications and Industry Impact
Shutter door profiles manufactured through roll forming serve diverse sectors:
- Residential security doors: Combining aesthetics with protection
- Commercial storefronts: Retail security closures
- Industrial facilities: Large-scale doors for warehouses and factories
- Specialized applications: Fire-rated shutters, blast-resistant designs, and hygienic closures for food processing
8. Selection Criteria and Operational Considerations
When evaluating shutter door roll forming machines, manufacturers consider:
- Production volume requirements: Determining machine capacity and automation level
- Material specifications: Compatibility with various coatings and alloys
- Profile complexity: Number of roll stands required
- Floor space and utility requirements
- Tooling investment and changeover flexibility
- Local technical support and service availability
9. Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Contemporary machines address environmental concerns through:
- Material efficiency with optimized nesting and minimal scrap
- Energy-efficient drives and regenerative systems
- Compatibility with recycled metal content
- Reduced VOC emissions compared to alternative manufacturing
- Long tooling life through advanced materials and coatings
10. Conclusion
The shutter door roll forming machine exemplifies the convergence of mechanical engineering precision, production automation, and material science innovation. By transforming flat metal coils into precisely engineered closure components with remarkable efficiency, these machines have enabled the widespread availability of affordable, high-performance shutter doors globally. As architectural demands evolve toward greater energy efficiency, smarter integration, and enhanced aesthetics, roll forming technology continues to advance—incorporating digital controls, adaptive tooling, and sustainable practices. The future will likely see further integration with building information modeling (BIM) systems, AI-driven optimization of production parameters, and development of new composite materials, ensuring that roll forming remains at the forefront of closure manufacturing technology.
The continued refinement of shutter door roll forming machines not only drives economic value through manufacturing efficiency but also contributes to built environment quality by enabling more secure, energy-efficient, and aesthetically pleasing architectural solutions across global markets.
Website:
www.greatforming.com (English)
www.arabicgreatforming.com (عربي)
www.russiangreatforming.com(Русский)
www.spanishgreatforming.com(Español)
www.frenchgreatforming.com(Français)
www.portuguesegreatforming.com(Portuguese)

